Microsoft Exchange Server is one of the most widely used email solutions. It offers a variety of features like calendar, contacts, tasks, and messaging, which are required by many organizations, small as well as large scale. In addition to it, Exchange also offers a web interface that can be accessed by all users, regardless of their mailbox location.
The web interface can be accessed remotely via a web browser, through a remote computer on the network. This makes the web interface vulnerable to cross-site scripting attacks, which can result in the execution of arbitrary script code on the targeted system. In addition to it, Exchange also provides the capability to connect to it via Outlook.
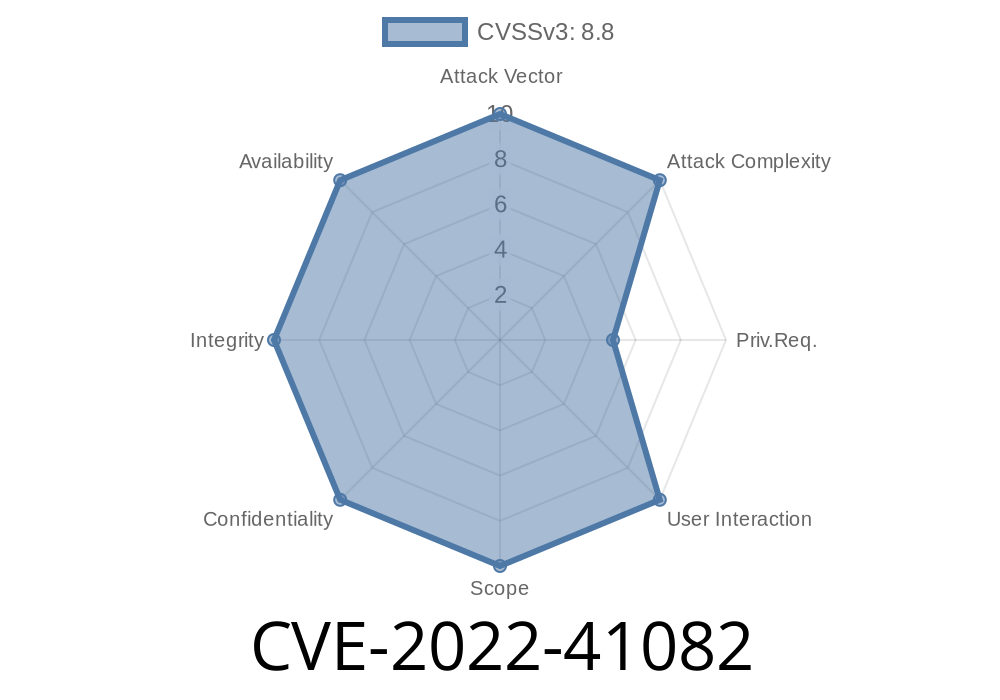
Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
The vulnerability is due to the remote code execution in Exchange Server and the ability to connect to it via Outlook. This allows an attacker to inject script code into the web interface, which can result in arbitrary code execution on the targeted system.
Exchange Server Vulnerabilities
Web interface:
The web interface is vulnerable to cross-site scripting attacks, which can result in the execution of arbitrary script code on the targeted system. In addition to it, Exchange also provides the capability to connect to it via Outlook.
Outlook:
Outlook is inherently vulnerable because it's a third party application and has support for ActiveX controls. These controls were developed by Microsoft in order to allow users control their data over the internet. They are also used by other applications such as Internet Explorer and are generally considered safe until they are exploited.
Exchange Server Cross Site Scripting and Outlook
Cross-site scripting attacks are becoming more and more common, with the latest being disclosed earlier this year. This vulnerability allows attackers to execute arbitrary script code on the targeted system. In addition, an attacker can also connect to Exchange via Outlook. This vulnerability has been exploited in the past by attackers to compromise email systems.
In order to prevent cross-site scripting attacks, you should restrict access to external web services that are not required for your organization. Additionally, when using Outlook (whether from within or outside of Exchange), you should use a firewall rule that requires users to specify their domain name before accessing external web services that are not required for your organization, like "www".
Overview of Exchange Web Interface Cross-site Scripting vulnerability
An attacker can use a Cross-site scripting vulnerability in the web interface of Exchange Server to execute arbitrary script code on the targeted system. This allows an attacker to download, upload, or change files on the server and send email messages from anywhere.
The bug was reported to Microsoft by security researchers of Websense technology company in November 2017. However, it is not clear whether this vulnerability is actively exploited in the wild.
Exchange Server – Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
A remote code execution vulnerability was discovered in Microsoft Exchange Server. The vulnerability exists in Windows PowerShell and Microsoft Office Web Apps (OWA) running on Exchange Server. Since the target system is Microsoft Outlook, a cross-site scripting attack is possible to exploit the vulnerability.
This vulnerability could be exploited by malicious users to execute arbitrary script code with low privilege on the targeted computer.
Timeline
Published on: 10/03/2022 01:15:00 UTC