When you think of database exploits, you may imagine complex attacks that cripple your system, steal all your information, or demand bitcoin. But real-world exploits are sometimes far more subtle—like the recently patched CVE-2024-21209, which affects Oracle MySQL Client’s popular mysqldump tool. This vulnerability doesn’t cause fireworks, but it _does_ have the power to leak information when you least expect it — especially with some misleading user action.
Let's break it down in simple terms, including exactly how an attacker could exploit it, code snippets, affected versions, and what you should do about it.
What is CVE-2024-21209?
CVE-2024-21209 is a security bug in MySQL’s mysqldump found in MySQL Client. Supported versions affected:
9..1 and earlier
It's present in the Client: mysqldump component.
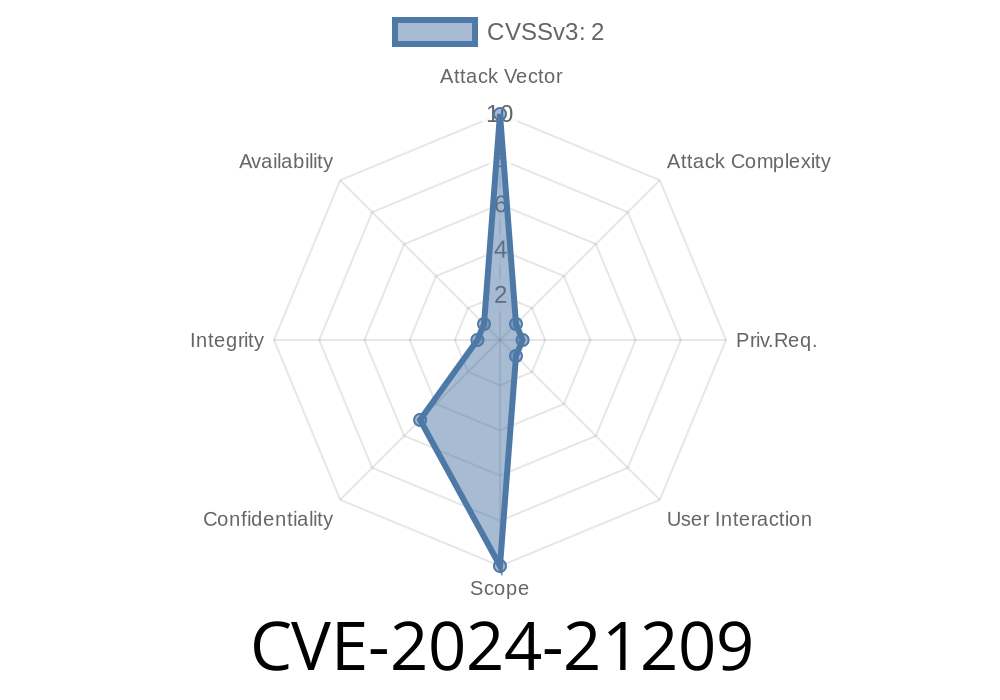
CVSS 3.1 Base Score: 2. (Low)
- Vector: (CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:H/PR:H/UI:R/S:U/C:L/I:N/A:N)
While the base score is low, it can be used for unauthorized _read_ access to certain data in your MySQL setup if your workflow enables it to.
Have high privileges and network access.
- Need a different user to interact with a malicious file or data (i.e., some social engineering is involved).
An attacker can’t just trigger this alone—they need you (or someone on your team) to do something, like running mysqldump on some crafted database or file.
The impact? An attacker could coax you into running mysqldump which might leak data you didn’t intend to leak by mishandling certain data during the export process.
Technical Details – How Does the Exploit Work?
mysqldump is used to output logical backups, but its parsing of certain inputs can be insecure in edge cases. Here’s a simplified example of how things might go wrong:
Exploit Scenario
Suppose an attacker is able to create a database/table or rows with "tricky" names or data.
Let’s say, for example, a table name is crafted or includes specific characters/sequences. When you as an admin run something like:
mysqldump -h attacker-controlled-host -u youruser -p yourdatabase > backup.sql
If the malicious remote server responds in a tricky way (for example, sending a SQL query with embedded secrets or obfuscated data), mysqldump could potentially “dump” information not intended for the output, or include hidden data from the connection, which could later be accessed by the attacker.
Example: Trick Table Name
CREATE TABLE information_schema.innodb_table_stats; -- (id int);
-- The above line attempts to play tricks with parser, comments, and schema names.
When you run mysqldump, this could lead to data or queries leaking into the dump, especially if the script processing the dump later makes wrong assumptions.
Or, an attacker could set up a database with information mixed into object names, so when dumped, the object names leak info.
Exploit Code Snippet
Suppose the attacker wants to hide something in table names or column defaults, which gets picked up by mysqldump:
USE test;
CREATE TABLE leaked_data_123_SECRETINFO (
id int,
value varchar(255)
);
When mysqldump is run
mysqldump -h malicious-host -u admin -p test
The dump output will contain leaked_data_123_SECRETINFO. If the attacker set up the host so this table name or its metadata is crafted to include secret tokens or data, the output will then "leak" that info out. If the dump is then shared, the secret goes with it.
Full Exploit Steps
1. Attacker sets up a MySQL server with malicious metadata (in table names/data).
2. Attacker convinces/victims script connects to this server (for instance, via a misconfigured host in scripts).
Victim runs mysqldump and saves the output.
4. mysqldump includes the attacker-inserted information in the dump, which can then be read by anyone with access to the dump file, leaking information.
Real-World Harm
- Limited Leak: This is not a massive, full-database exposure. Only _some_ information could leak—specifically, what an attacker can sneak into object names/data readable by mysqldump.
- Requires Social Engineering: The attacker needs you to "do something"—it's not triggered automatically.
- No Integrity/Availability Impact: This is all about leaking information. No data is overwritten or deleted, and mysqldump won’t crash.
How To Protect Yourself
- Update your MySQL clients ASAP: Oracle CPU Advisory for CVE-2024-21209
Official References
- Oracle Advisory: CVE-2024-21209
- Oracle CPU Advisory: https://www.oracle.com/security-alerts/cpujul2024.html
Conclusion
CVE-2024-21209 isn't going to let someone walk away with your whole database overnight. But it _can_ become a tool for a sophisticated attacker with access and some social skills, especially if an admin is tricked into running tools with untrusted input or against an attacker-controlled server. Like all security bugs, it’s best to patch and be careful—never underestimate the clever ways attackers can abuse even small leaks!
Timeline
Published on: 10/15/2024 20:15:09 UTC
Last modified on: 11/21/2024 08:53:58 UTC